2. D-RTK Base Station Guide#
2.1. Introduction#
2.1.1. What Is an RTK Station#
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) positioning is a satellite navigation technique used to enhance the accuracy of GNSS measurements. An RTK station operates as a reference point with a known or precisely calculated position. By comparing its known position to the position calculated from satellite signals, the station generates correction data that is transmitted in real time to a drone.
Unlike standard GNSS, which typically provides meter-level accuracy due to atmospheric errors, satellite clock drift, and signal noise, RTK uses real-time corrections to compensate for these errors. This allows RTK-enabled systems to achieve centimeter-level horizontal and vertical accuracy.
Within the DJI ecosystem, the D-RTK 3 serves as a high-precision GNSS reference station that supplies correction data directly to compatible DJI aircraft and controllers.
2.1.2. Use Cases#
The DJI D-RTK 3 is designed for professional applications where high positional accuracy is essential, including aerial mapping and photogrammetry, surveying, and other high precision applications. By providing reliable RTK corrections, the D-RTK 3 enhances data accuracy, reduces the need for ground control points, and improves overall operational efficiency.
2.2. Prerequisites#
Compatible DJI drone equipped with an integrated RTK module or RTK antenna
The full capabilities of the D-RTK3 station can be used with a DJI 4th generation drone (DJI M400, M4E/4T, M4D/4TD). The station can be set up with manual calibration, with the help of a custom network (NTRIP) and using Precise Point Positioning (PPP). Using older drones and controllers the station does not support PPP and only supports base station mode.
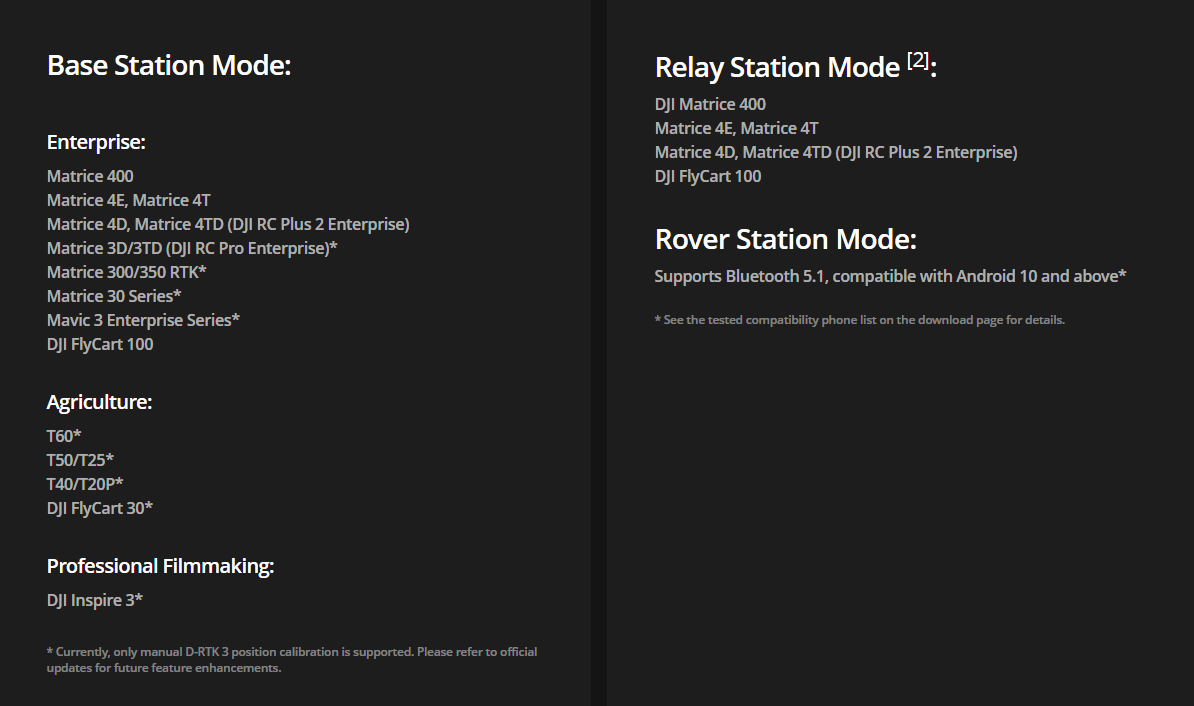
Currently supported models with D-RTK3 station ((check for current information: https://enterprise.dji.com/d-rtk-3))#
Required accessories (tripod, mounting pole)
DJI Pilot 2 for connecting the RTK to the drone and configuring settings
DJI Enterprise 2 for firmware updates, coordinate system configuration, and Rover Station mode
UgCS Companion for flying SkyHub missions
2.3. First Activation#
2.3.1. Charging and turn on procedure#
Charge the device before powering on for the first time. Make sure to use a PD3.0 USB charger with 9 to 15 V voltage, such as a DJI 65W portable charger. Once it is charged the battery symbol will turn green. Then press, and press and hold the power button to turn on the device.
2.3.2. Activation and initial firmware update#
The product needs to be activated before first use.
When used as a base or relay station, it can be activated by following prompts in DJI Pilot 2 when connecting to the drone and the controller if it has internet connection.
When used as a rover station, you need to download DJI Assistant 2 (Enterprise Series) and connect the D-RTK3 station to a computer using a USB-C cable. Activate the device in DJI Assistant 2.
2.4. Indicators and Status Information#
2.4.1. Battery Indicators#

2.4.2. Operating Modes#
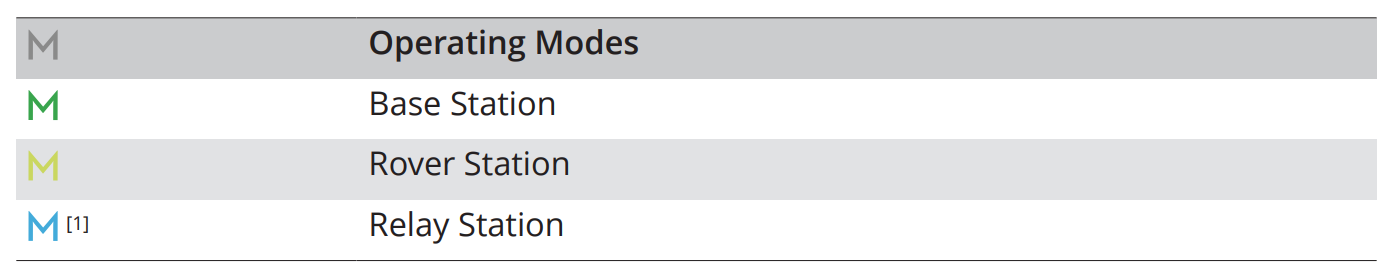
2.4.2.1. Base Station Mode#
In Base Station Mode, the D-RTK 3 operates as a fixed reference station that continuously calculates RTK correction data based on its known or averaged position. These corrections are transmitted in real time to compatible DJI aircraft to improve positioning accuracy during flight. This results in consistent absolute accuracy across multiple flights and reduced reliance on ground control points.
2.4.2.2. Relay Station Mode#
Relay Station Mode is used to extend communication and RTK correction coverage between the base station and the aircraft. It is particularly useful in large operational areas or environments where terrain, vegetation, or structures may obstruct direct signal transmission. For optimal performance, the relay station should be positioned at an elevated location with clear visibility to both the base station and the aircraft.
2.4.2.3. Rover Station Mode#
In Rover Station Mode, the D-RTK 3 functions as a mobile GNSS receiver for collecting high-precision ground measurements. This mode is typically used for surveying tasks such as recording ground control points or check points.
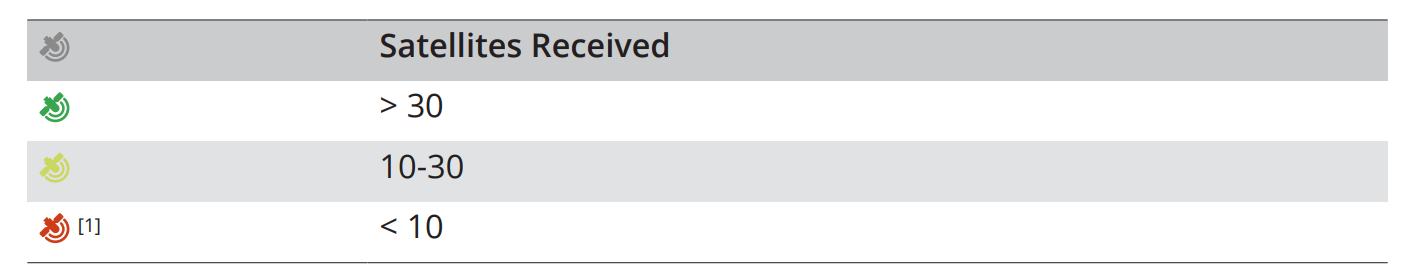
2.4.3. GNSS Signal Indicators#
2.5. Base Station Setup#
The station requires a wide field of view. Make sure to place the device so that there are no obstructions within a 15 degree angle above the horizontal plane of the antennas to prevent GNSS signals to be blocked. The location should be at least 200m from high-power radio emission sources (television stations, microwave stations, etc.) and at least 50m away from high voltage transmission lines to avoid electromagnetic interference. The location also should be away from large bodies of water or objects that strongly interfere with satellite signal reception.
Use the survey pole and tripod kit (if you have one) to set up the station. Make sure it is level according to the built in leveller.
You can consult the DJI manual for further information: https://dl.djicdn.com/downloads/d-rtk-3/UM/20250116/D-RTK-3_User%20Manual_v1.0_en.pdf
2.6. Connecting to DJI M400 or another 4th generation DJI drone#
Set up the D-RTK3 station and turn it on by pressing, and then pressing and holding the power button.
Turn on the drone and the remote controller.
Start DJI Pilot 2 and head over to Settings and select Precise Positioning Setting
Enable RTK Positioning
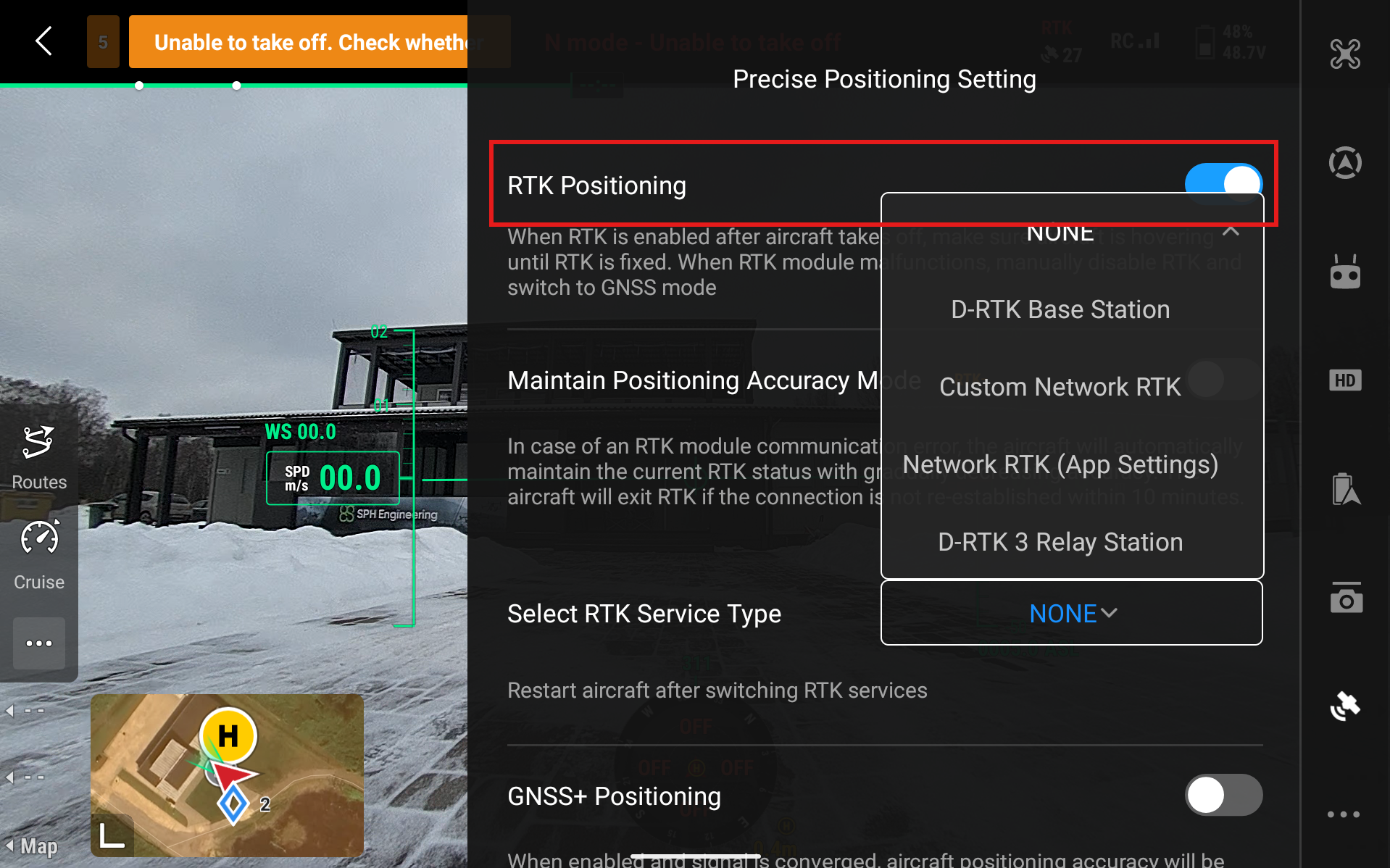
Select RTK Service Type and select D-RTK Base Station
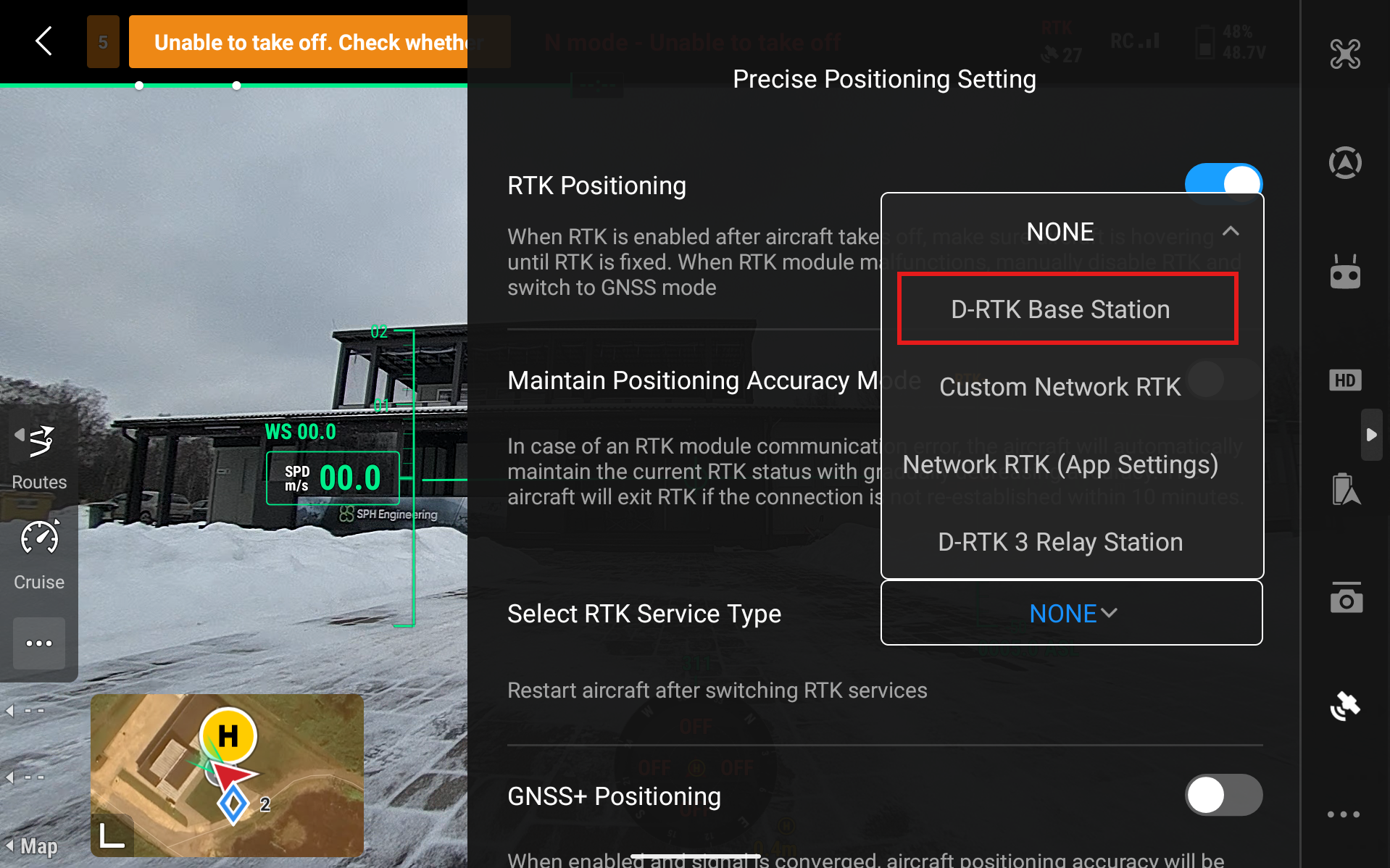
Click on Aircraft RTK Status - Not Connected
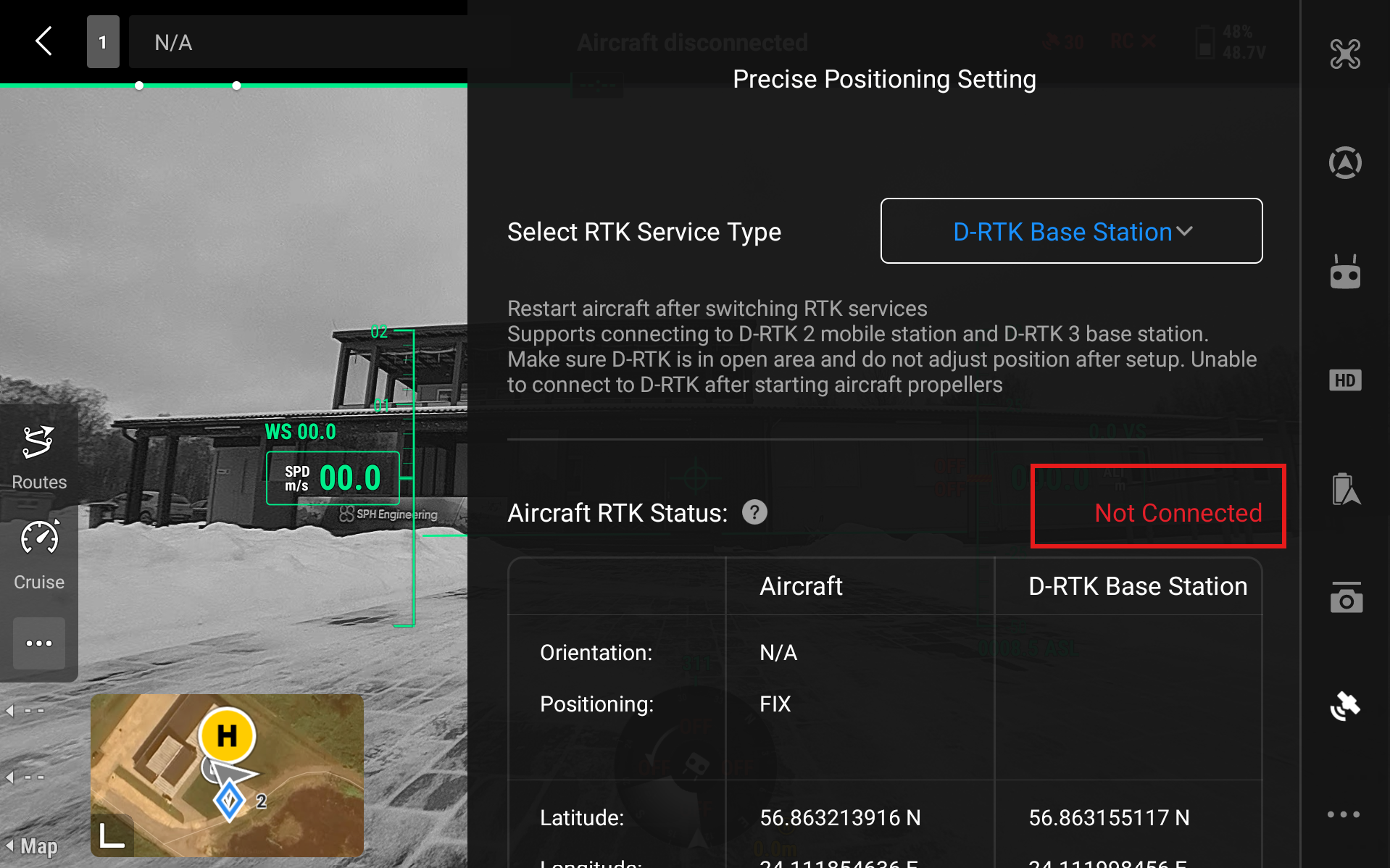
Select D-RTK Base Station - RTK3
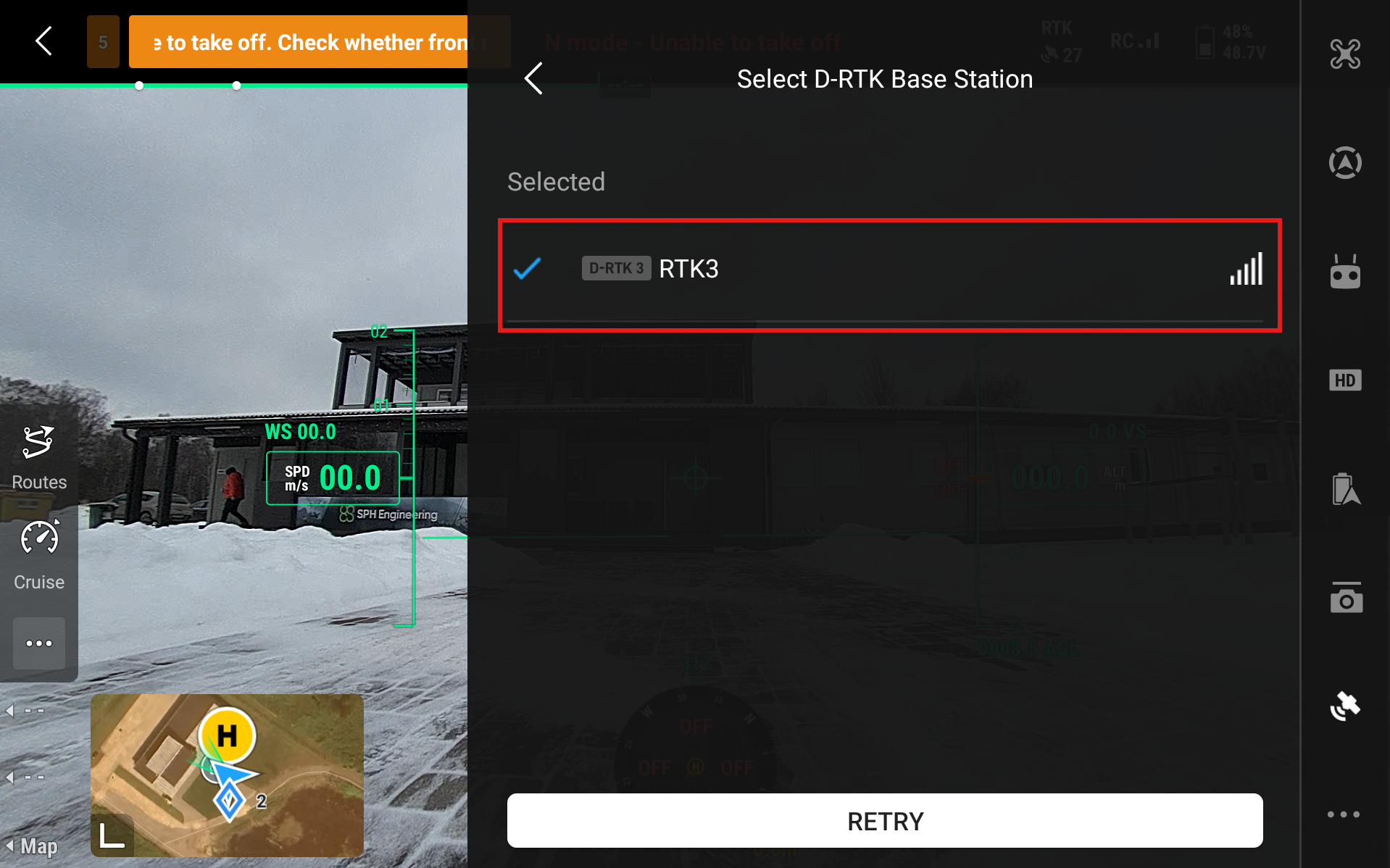
Aircraft RTK Status should start to show Converging and eventually turn to Connected (green). If the status stays on Converging for too long even when the drone has access to GNSS satellites (is outside in a clear area) then restart the drone and remote controller.
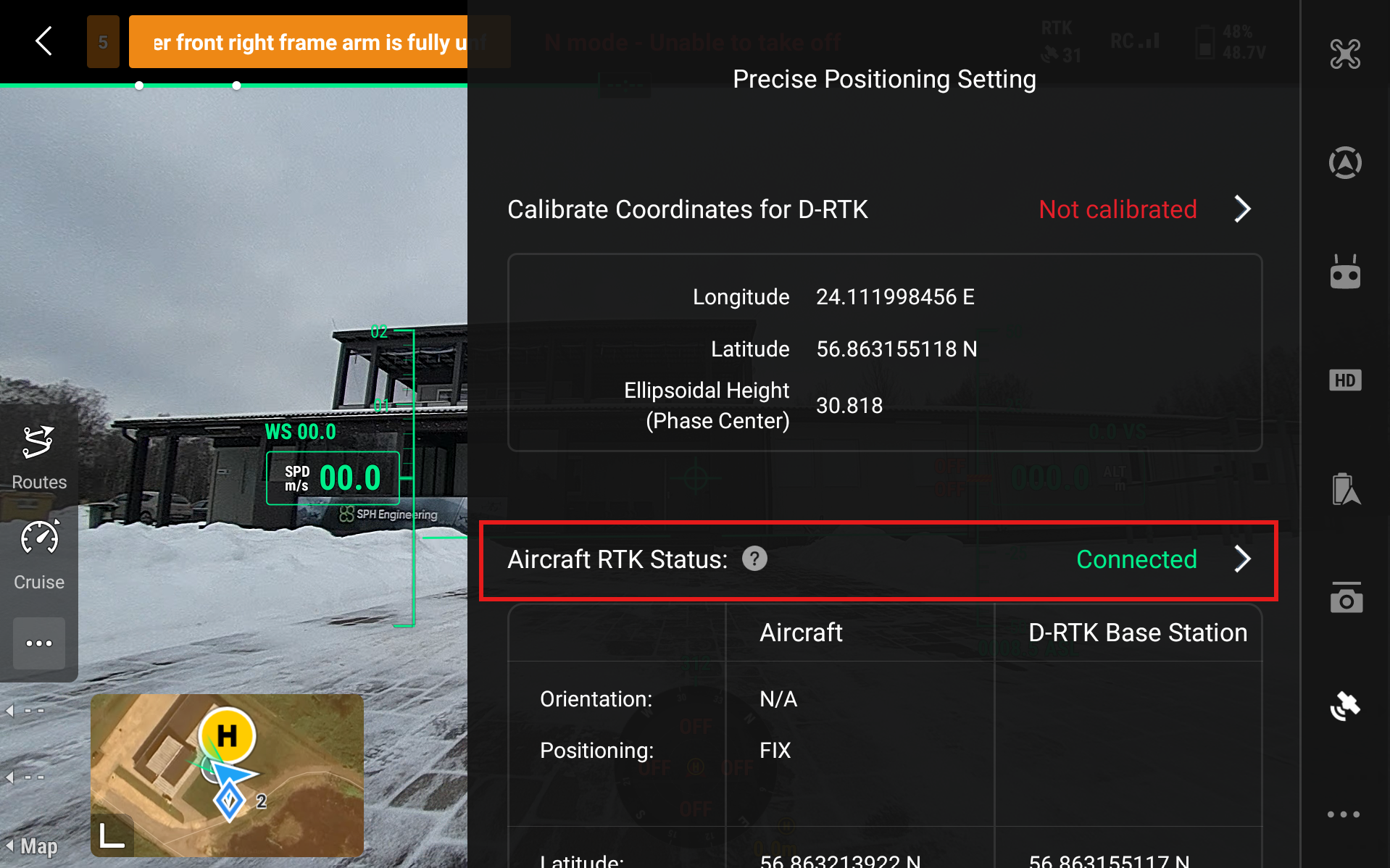
Now we need to calibrate the coordinates. Head to Calibrate Coordinates for D-RTK and press Not Calibrated.
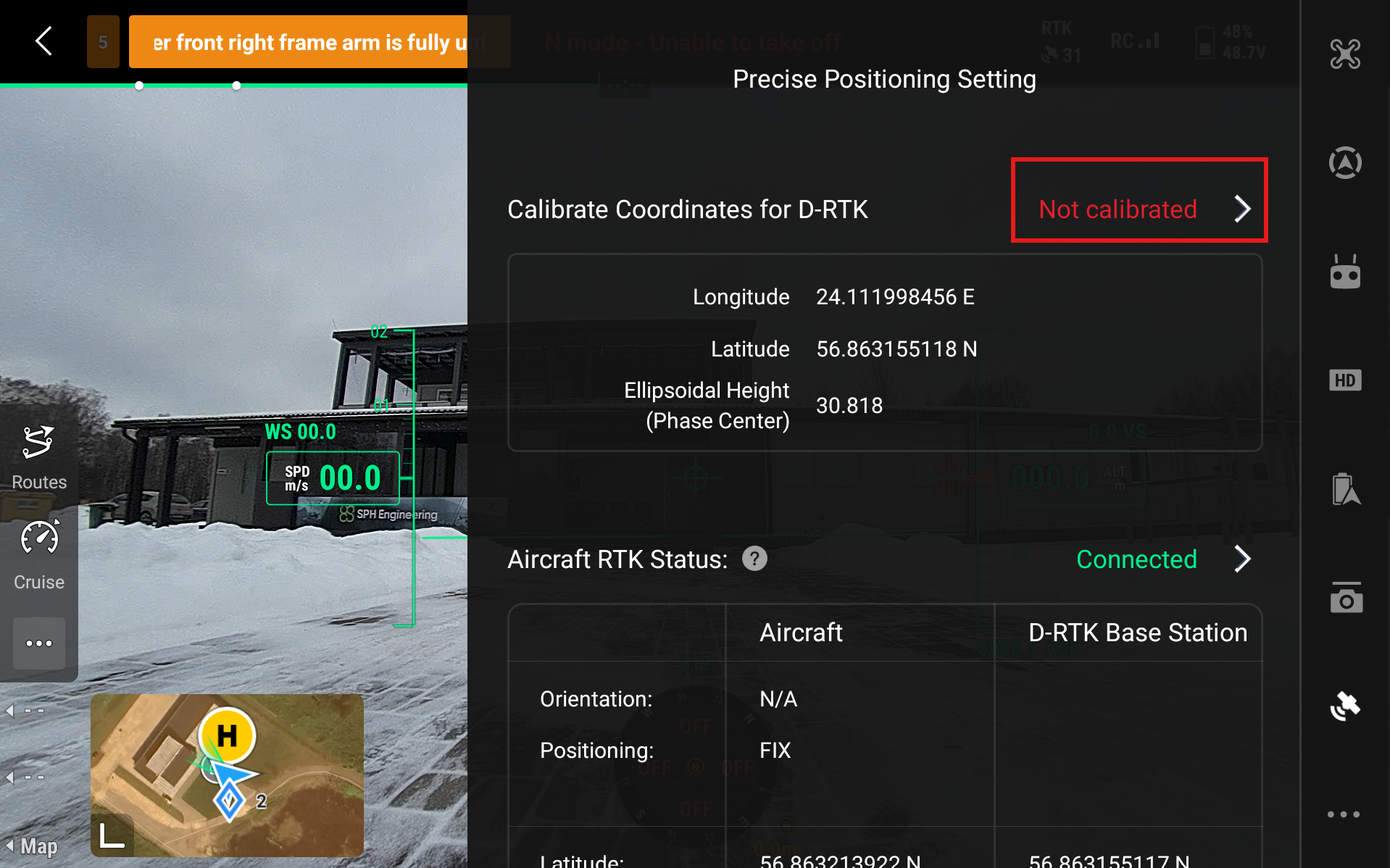
Select New
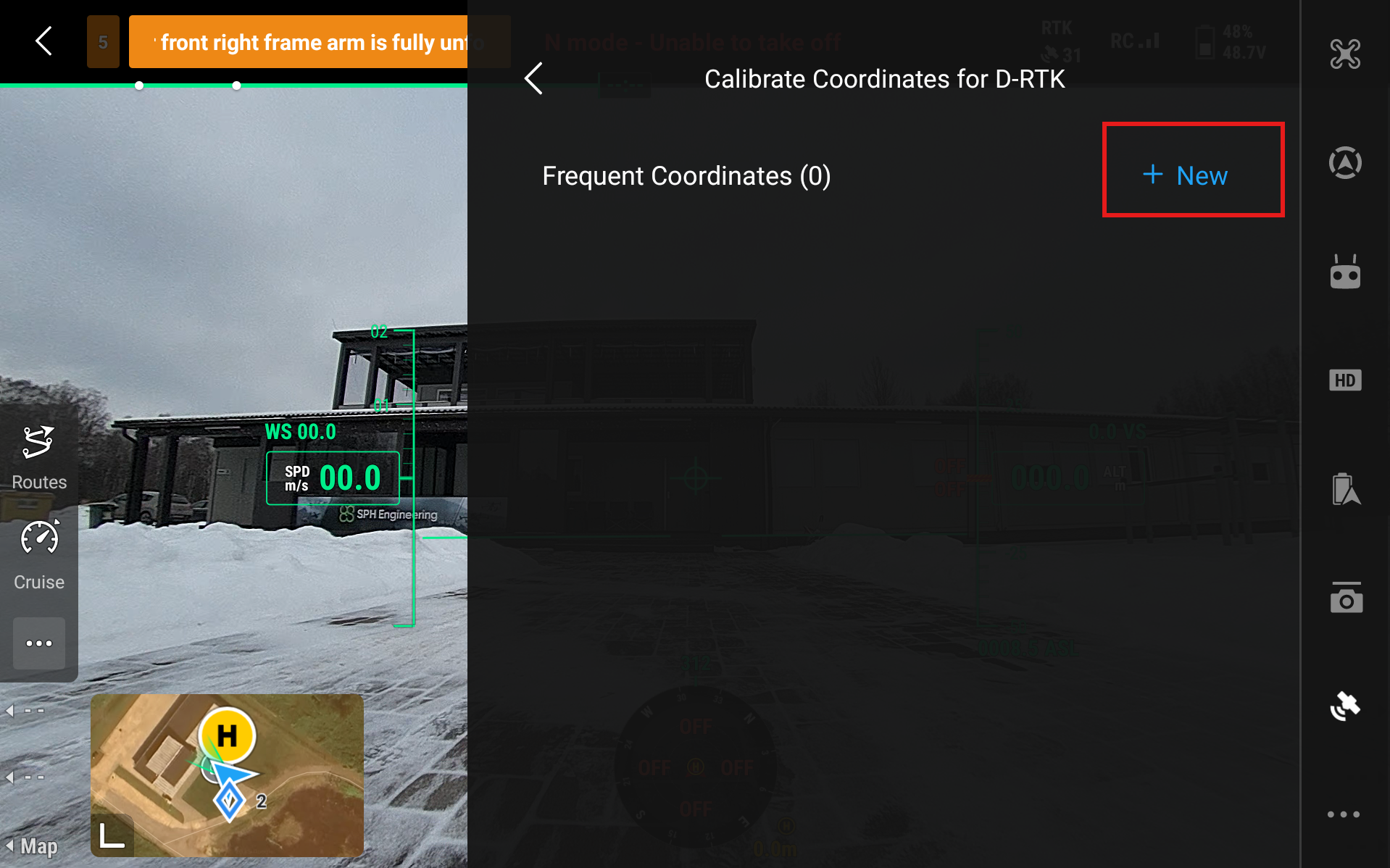
Now you have to choose the Source of Calibration. There are three ways to calibrate the station - Manual Calibration (if you know specific coordinates of the station), Custom Network RTK or NTRIP (if you have access to a service) and Precise Point Positioning or PPP (longer calibration time but quite precise).
11.1. Manual Calibration
Use this only if you know precise coordinates of the D-RTK3 station. Then input these coordinates in the Longitude and Latitude sections. You can save them as Frequent Coordinates if you plan on using the same station location in further flights.
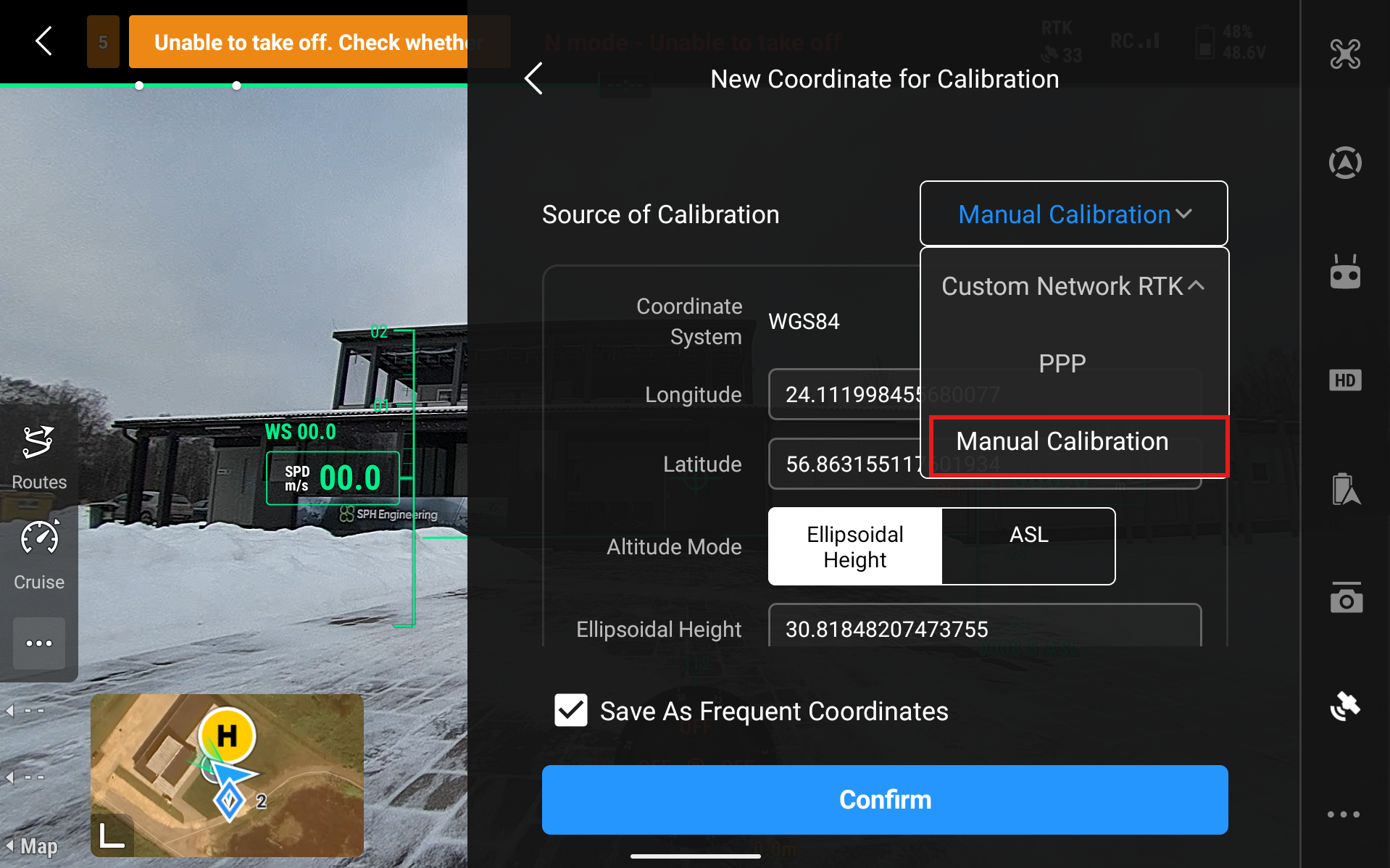
When you select Manual Calibration, then it will automatically generate some coordinates for the station but these are very imprecise. Our tests generally show a difference of 2-4 meters compared to the actual location. Here you can enter the Longitude and Latitude of the base station as well as its height.
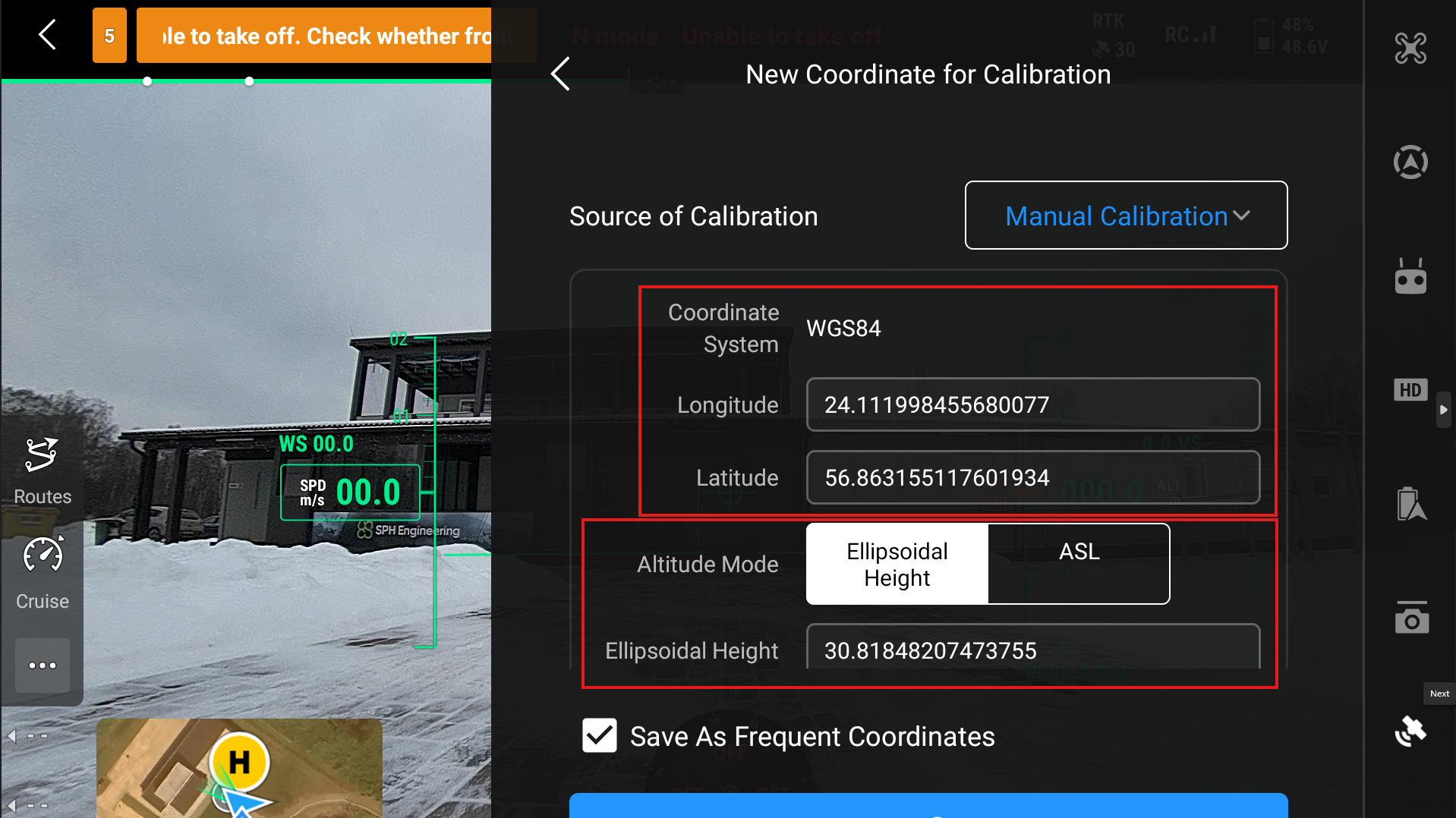
11.2. Custom Network RTK
The Custom Network RTK option should be used as the calibration source for the D-RTK 3 when a reliable third-party or regional RTK network is available. In this configuration, the D-RTK 3 receives correction data from an external RTK network via an internet connection and uses it to determine and maintain its reference position. Using a network RTK source allows for faster deployment of the station eliminating time spent on coordinate averaging. This method requires constant network connection.
In DJI Pilot 2, select Custom Network RTK as Source of Calibration and input the NTRIP Address, Port, Account, Password and Mount Point to use this method as a source of calibration.
11.3. Precise Point Positioning (PPP)
Precise Point Positioning (PPP) should be used as the calibration source for the D-RTK3 station when RTK correction services are unavailable or impractical, and a high level of absolute positioning accuracy is still required. PPP is particularly useful in remote or isolated locations where there is no access to cellular networks or permanent RTK infrastructure; it allows the D-RTK 3 to operate independently. PPP can also serve as a fallback calibration method when network RTK connections are unstable or unreliable.
While PPP does not typically achieve the same real-time centimeter-level accuracy as RTK, it provides stable decimeter-level positioning once convergence is reached. In DJI Pilot 2 it is possible to choose three accuracy levels - 100cm, 50cm, and 20cm Expected Horizontal Accuracy. In our tests, 100cm accuracy was done calibrating in around 5 minutes, 50 cm was done in around 10 minutes, and the 20cm - in 20 minutes. Depending on the situation, connection and access to GNSS, this process may take significantly longer.
To set up PPP in DJI Pilot 2, select PPP as the Source of Calibration. Then you need to select your expected horizontal accuracy and click on Start Calibration.
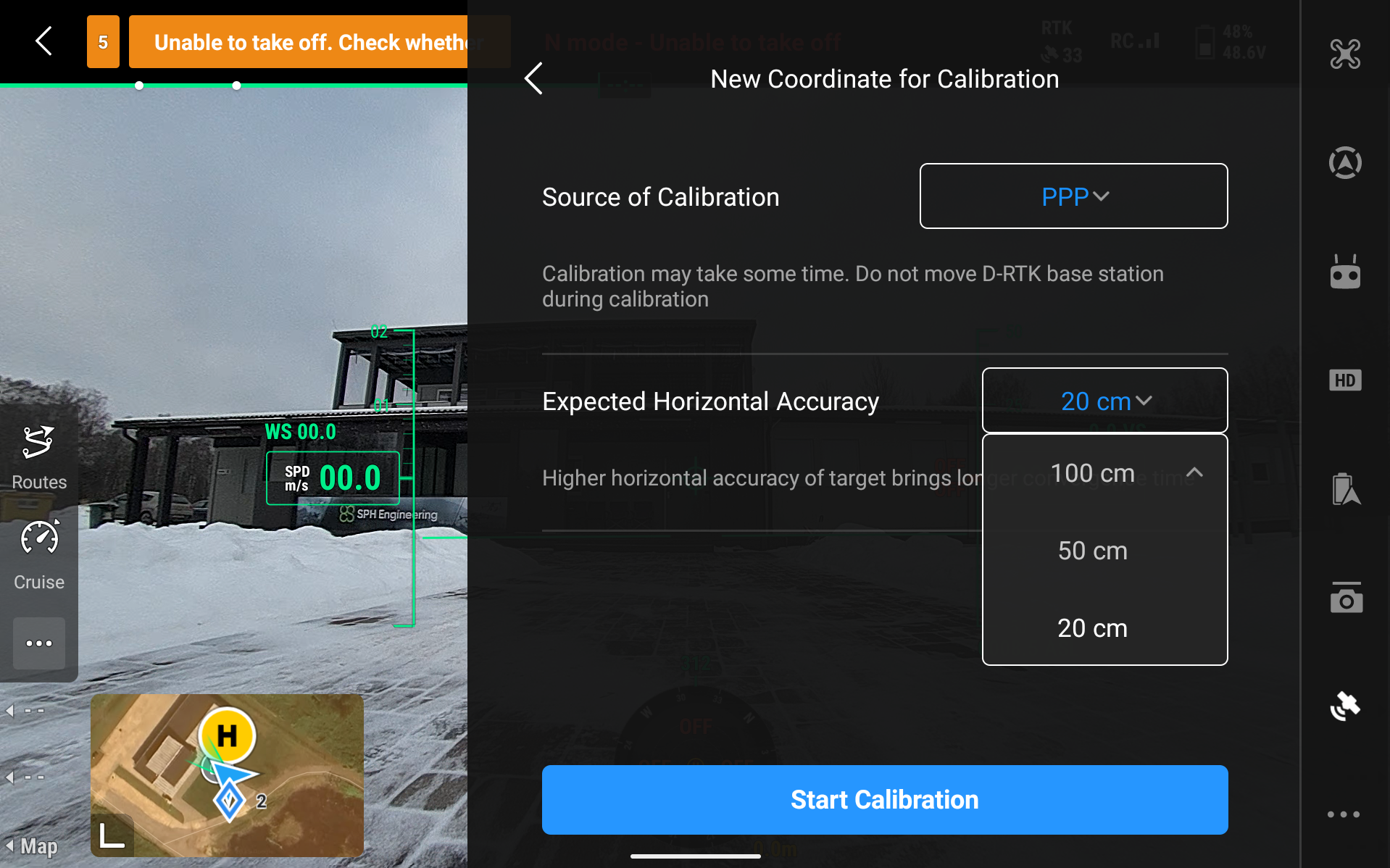
Then a calibration screen like this will pop up. It will take some time as mentioned before.
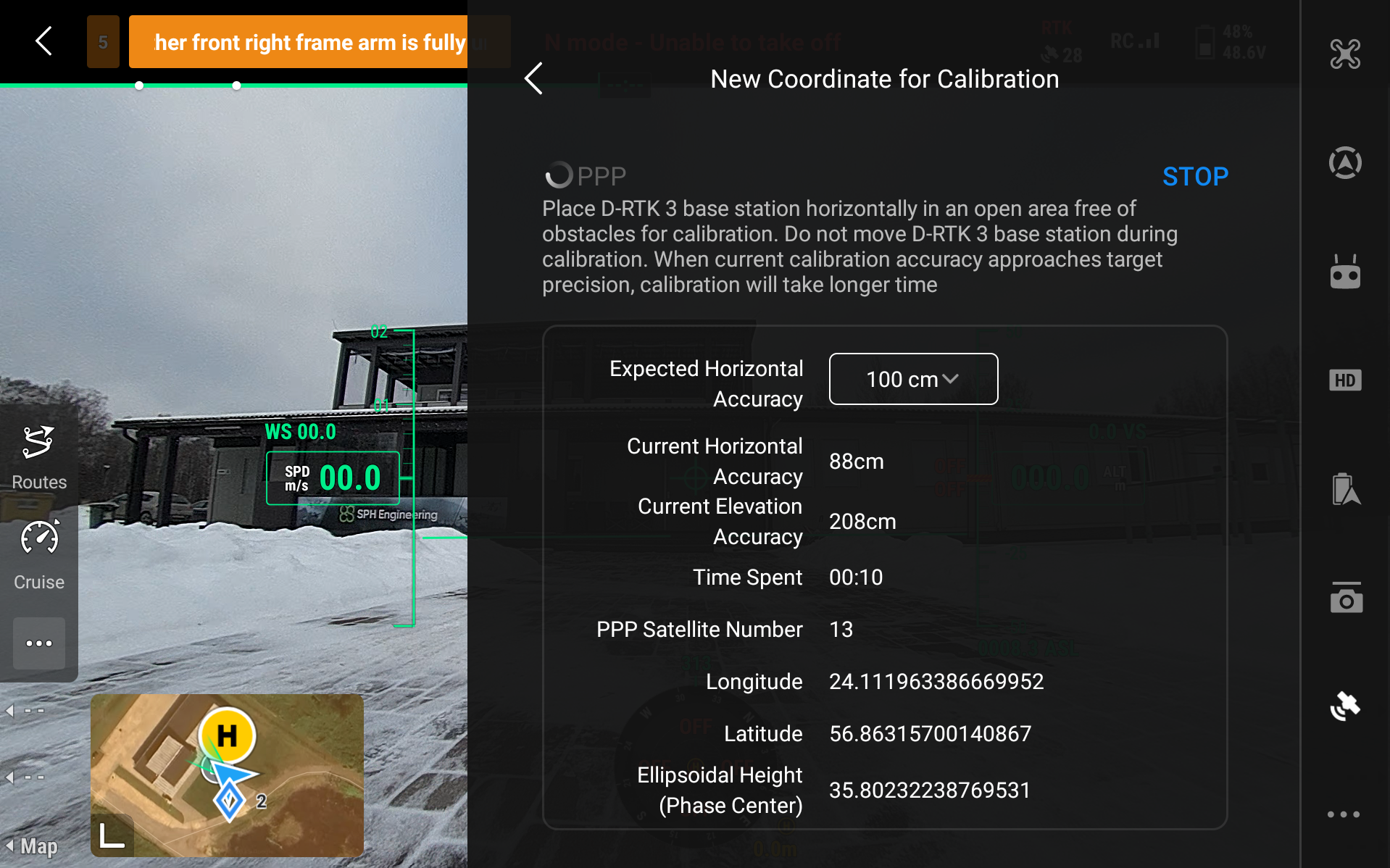
The process will automatically finish after some time and the calibrated coordinates will show up, which then you are able to save if necessary.
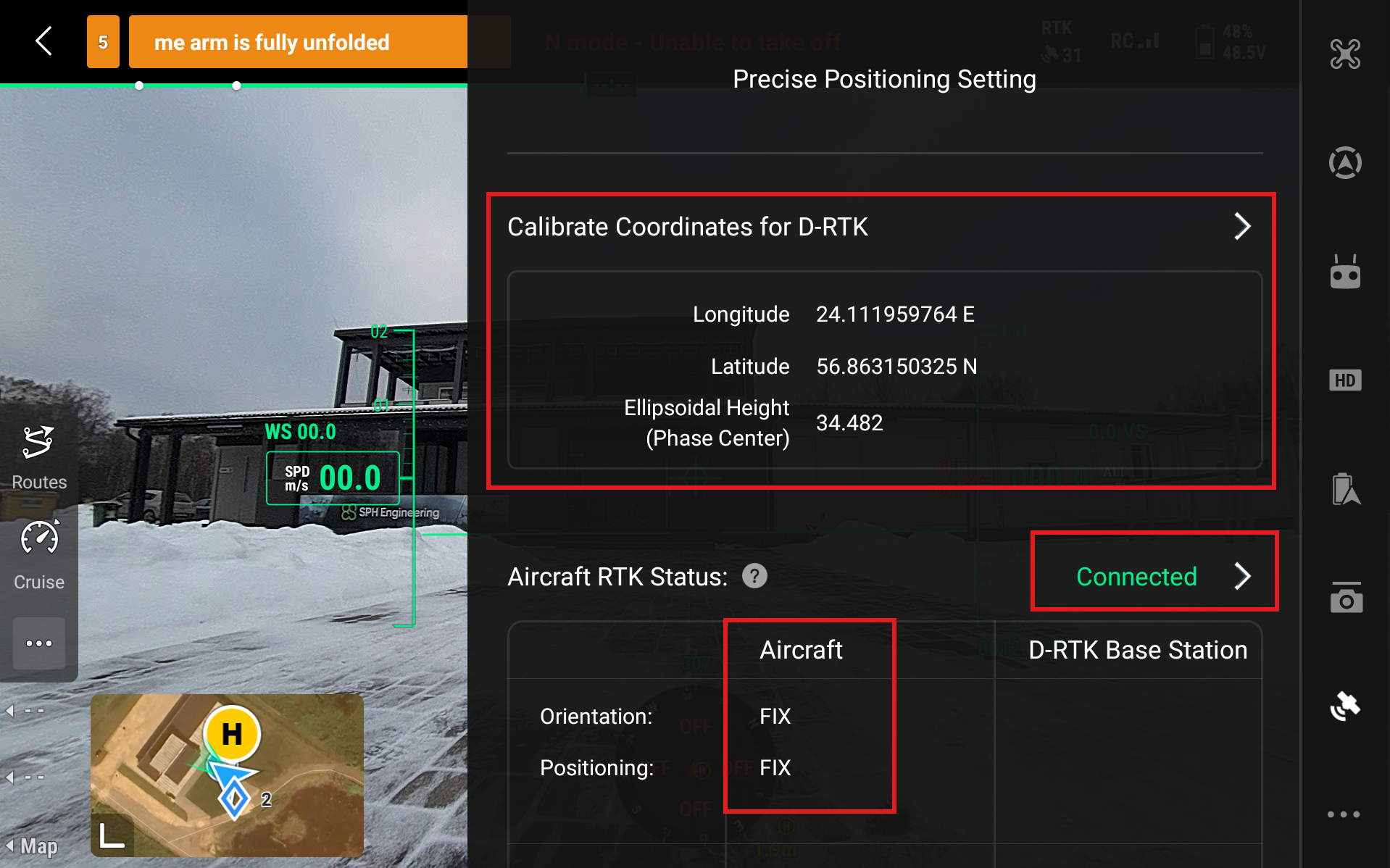
After calibrating the coordinates for D-RTK in any of the aforementioned ways, the Precise Positioning Setting should look like this.
Precise coordinates shown and no Not Calibrated option
Aircraft RTK Status - Connected
Aircraft FIX Positioning
If this is the case then the RTK is configured successfully.
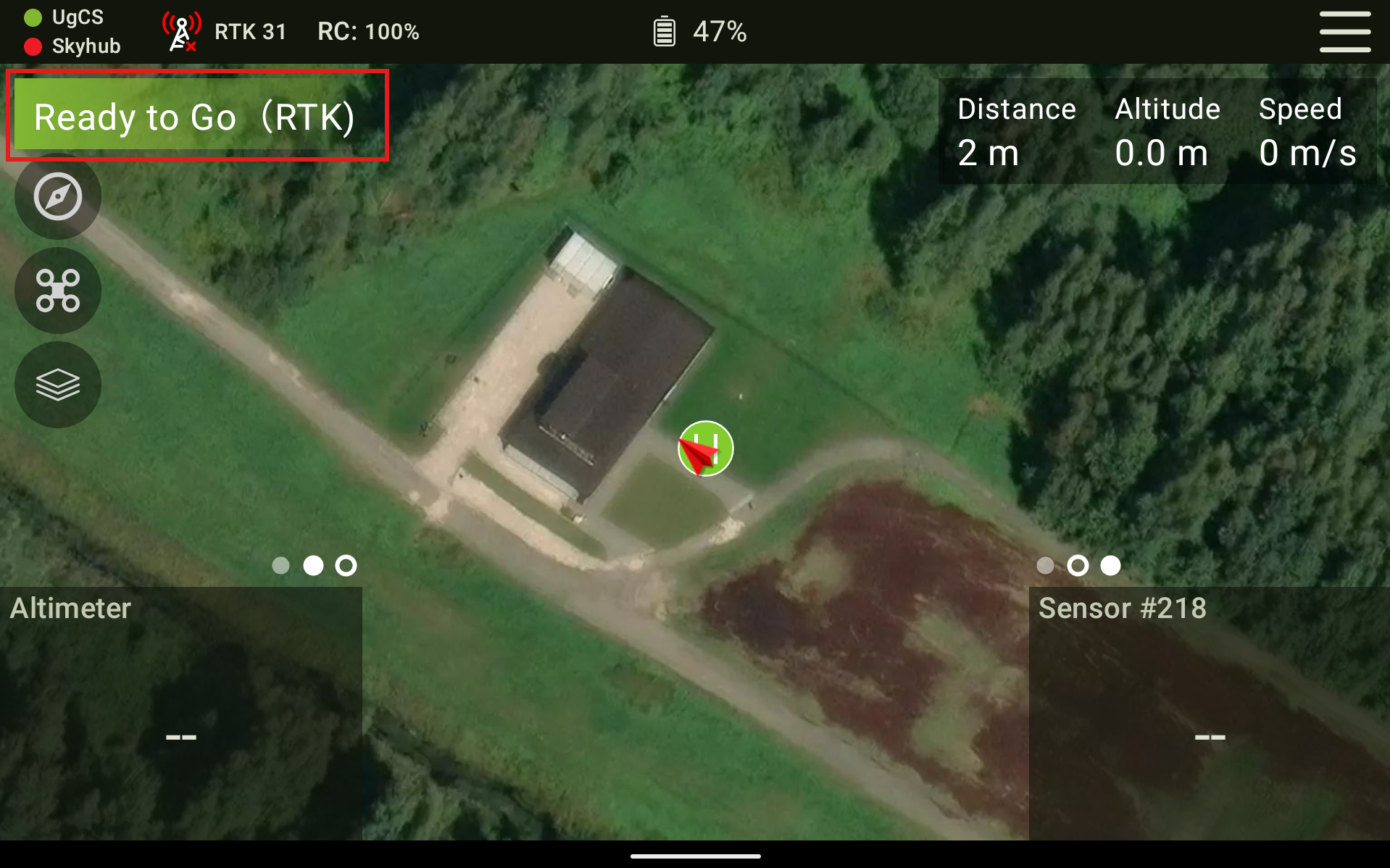
Now further information for if you are flying your mission with UgCS Companion. Firstly, close the DJI Pilot 2 application fully, so it is not running in the background. Then open up UgCS Companion and connect it to the drone as you normally would. If the drone is operational and ready to fly with RTK, it should show Ready to Go (RTK). And when pressing the RTK symbol at the top left of the screen, it shows RTK Status - Connected.
Note
If you are using an older version of UgCS Companion and when you click on the RTK symbol it shows RTK symbol - Unknown, then it is okay to continue only if the main screen in Companion shows Ready to Go RTK.
2.7. Connecting to DJI M300/M350 drones#
Using older DJI drones will require manual base station calibration. It is necessary to enter accurate coordinates for the D-RTK 3 station. These coordinates must represent the true geodetic position of the antenna reference point. There are two common approaches to obtain this information:
Using an Existing Geodetic Control Point. If a known geodetic (survey) control point is available near the planned base station location, its official coordinates can be obtained from the national or regional geodetic network authority. The D-RTK 3 antenna can then be positioned directly over this point, and the published coordinates can be entered into the system.
Measuring with Another RTK-Capable GNSS Receiver. A separate RTK-enabled GNSS receiver can be used to measure the base station position by connecting to a correction service via NTRIP. After achieving a fixed RTK solution, the measured coordinates can be recorded and used as the reference coordinates for the D-RTK 3 station.
If you do not have the resources to precisely measure the coordinates for the base station then this method is not recommended. Otherwise, it will automatically generate some coordinates for the station but these are very imprecise. Our tests generally show a difference of 2-4 meters compared to the actual location of the station.
Set up the D-RTK3 station and turn it on by pressing, and then pressing and holding the power button.
Turn on the drone and the remote controller.
Start DJI Pilot 2 and head over to Settings and select RTK
Enable RTK Positioning
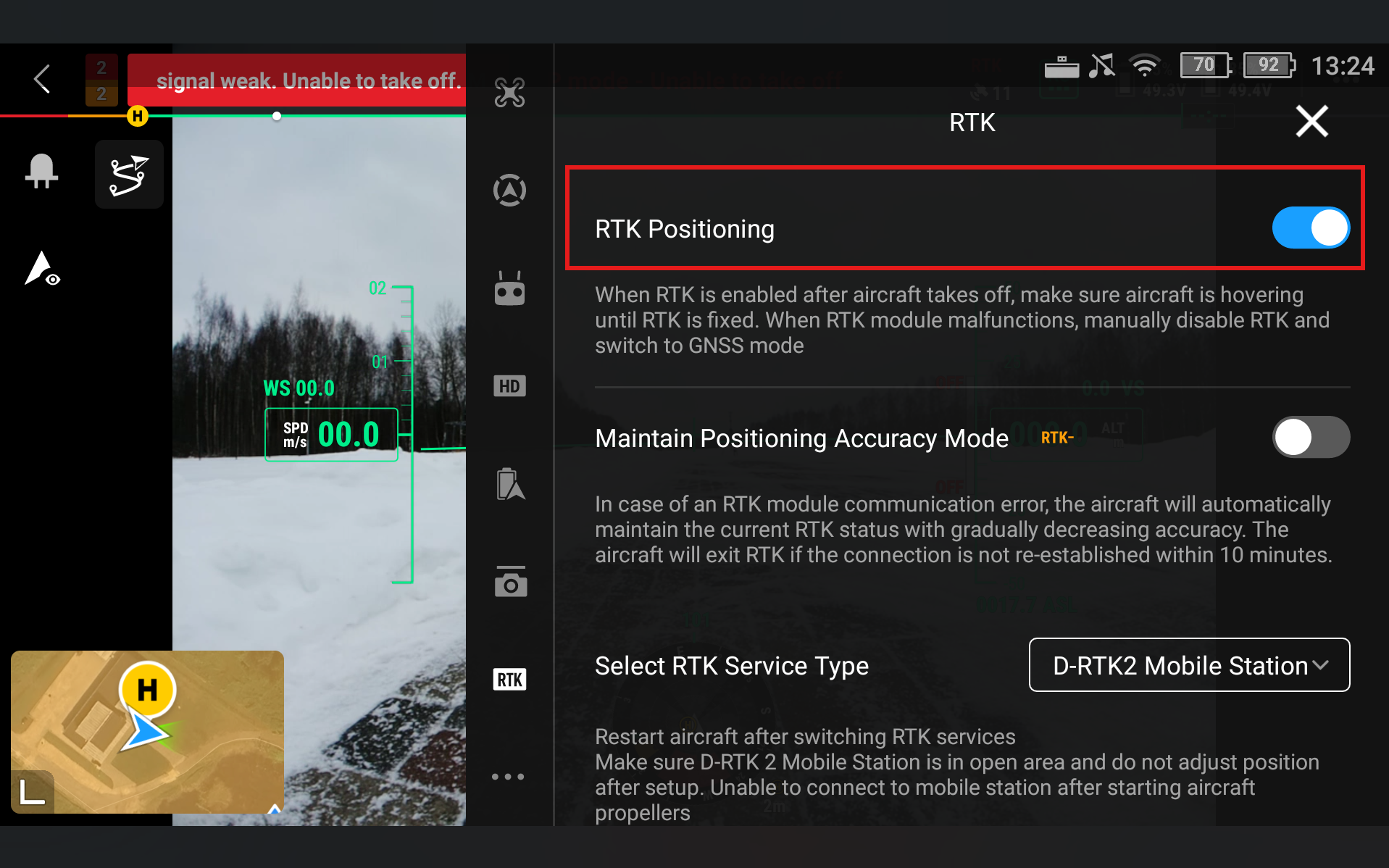
Go to RTK Service Type and select D-RTK2 Base Station
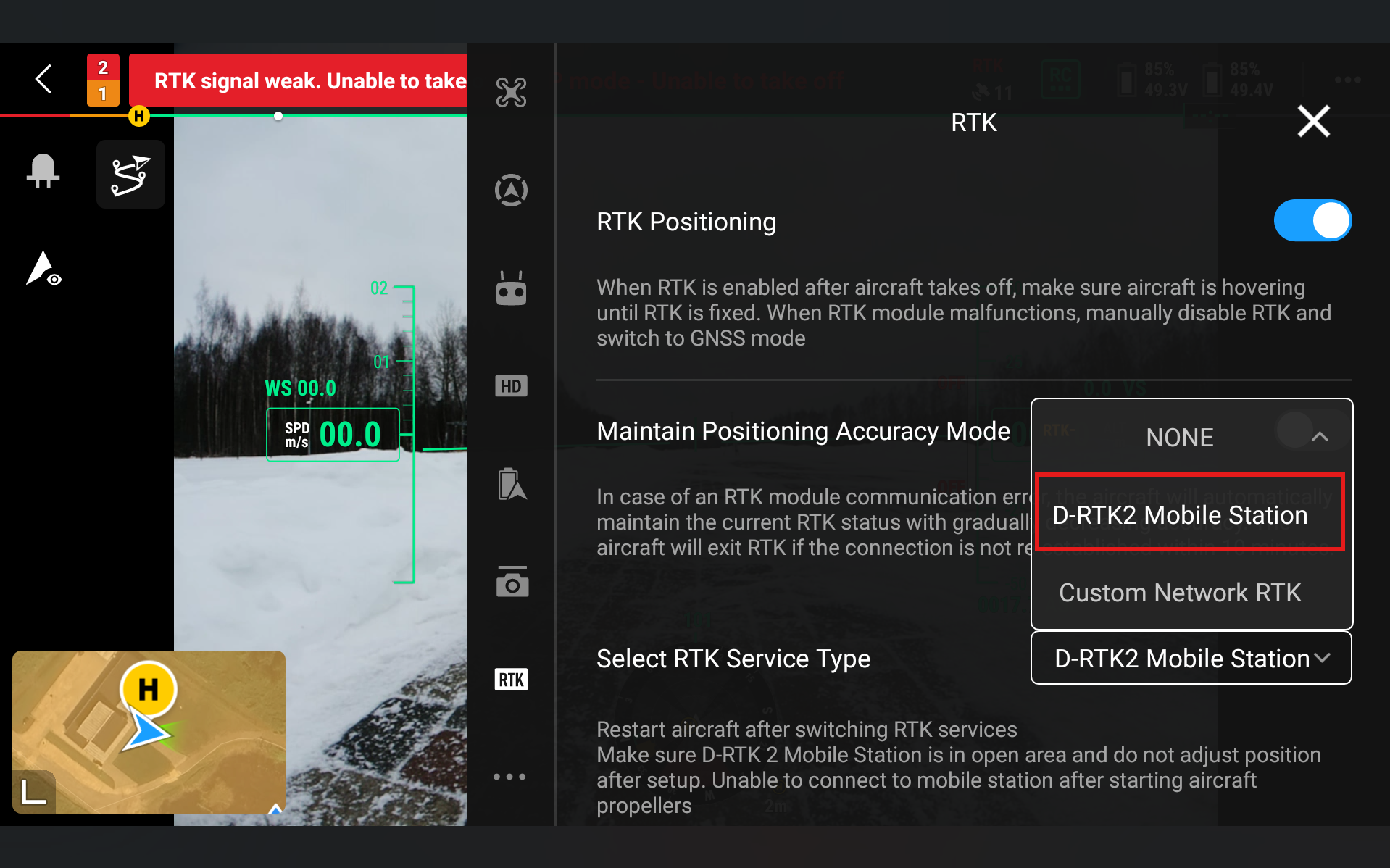
Go to Status and click Not Connected
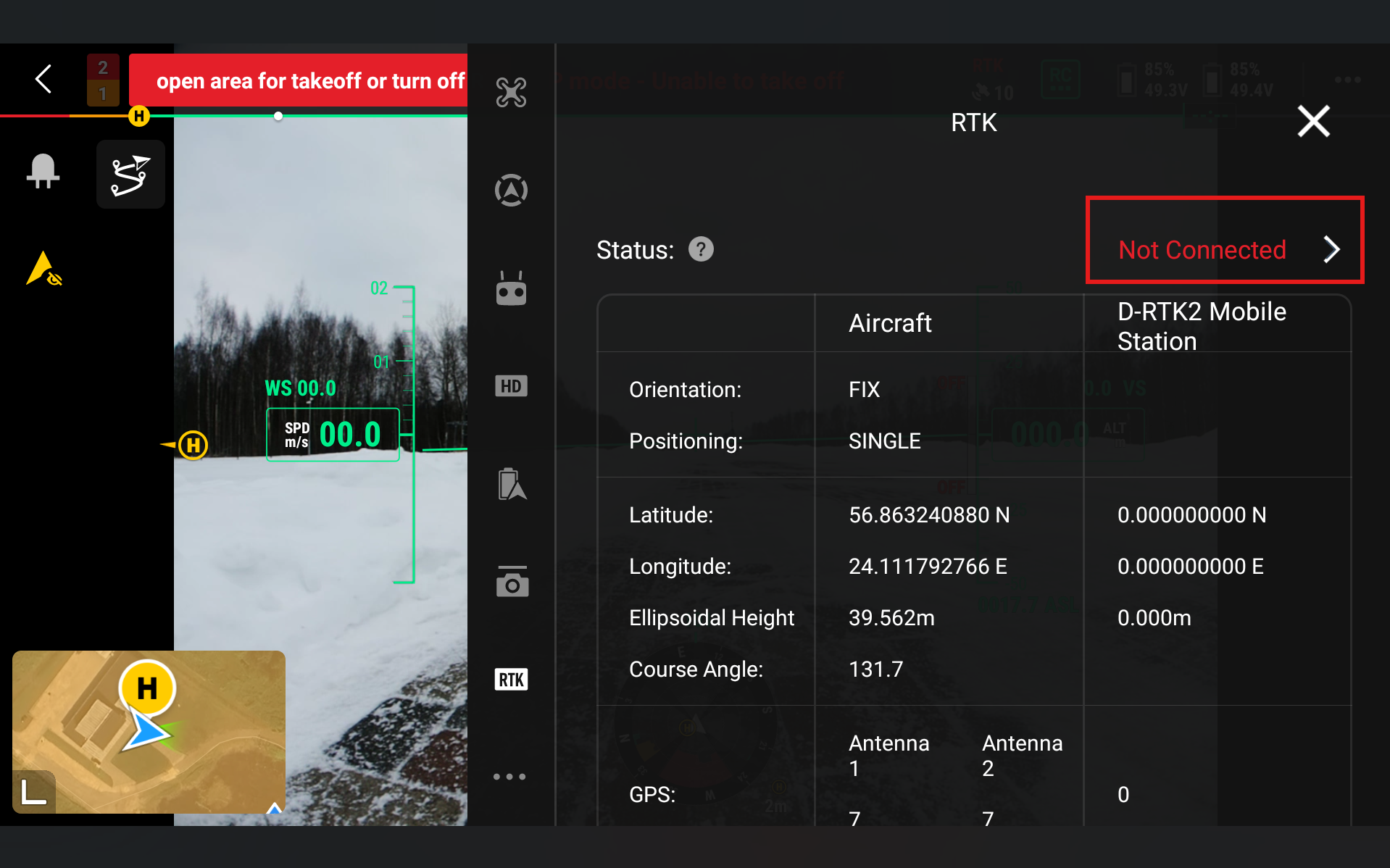
Select RTK3
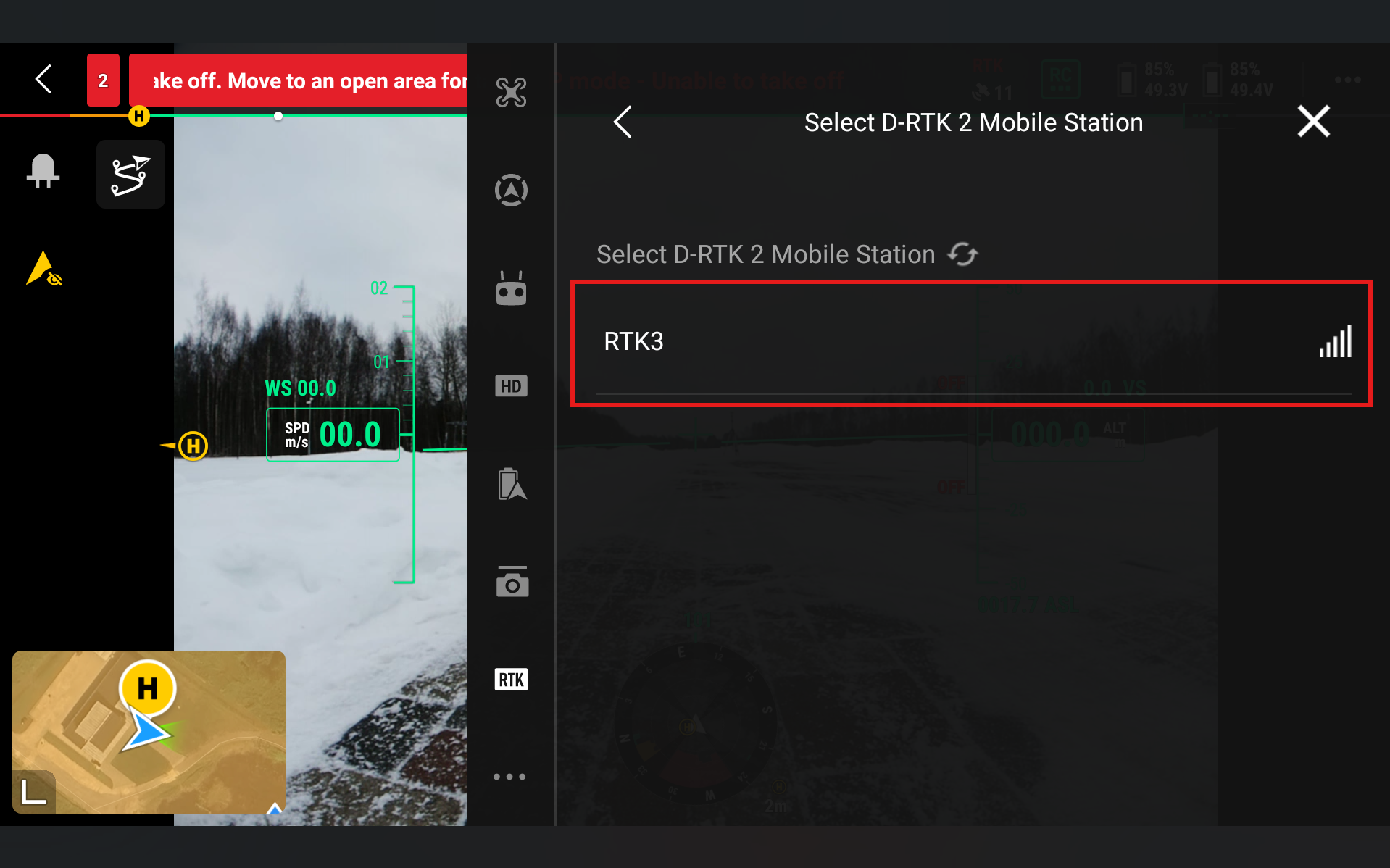
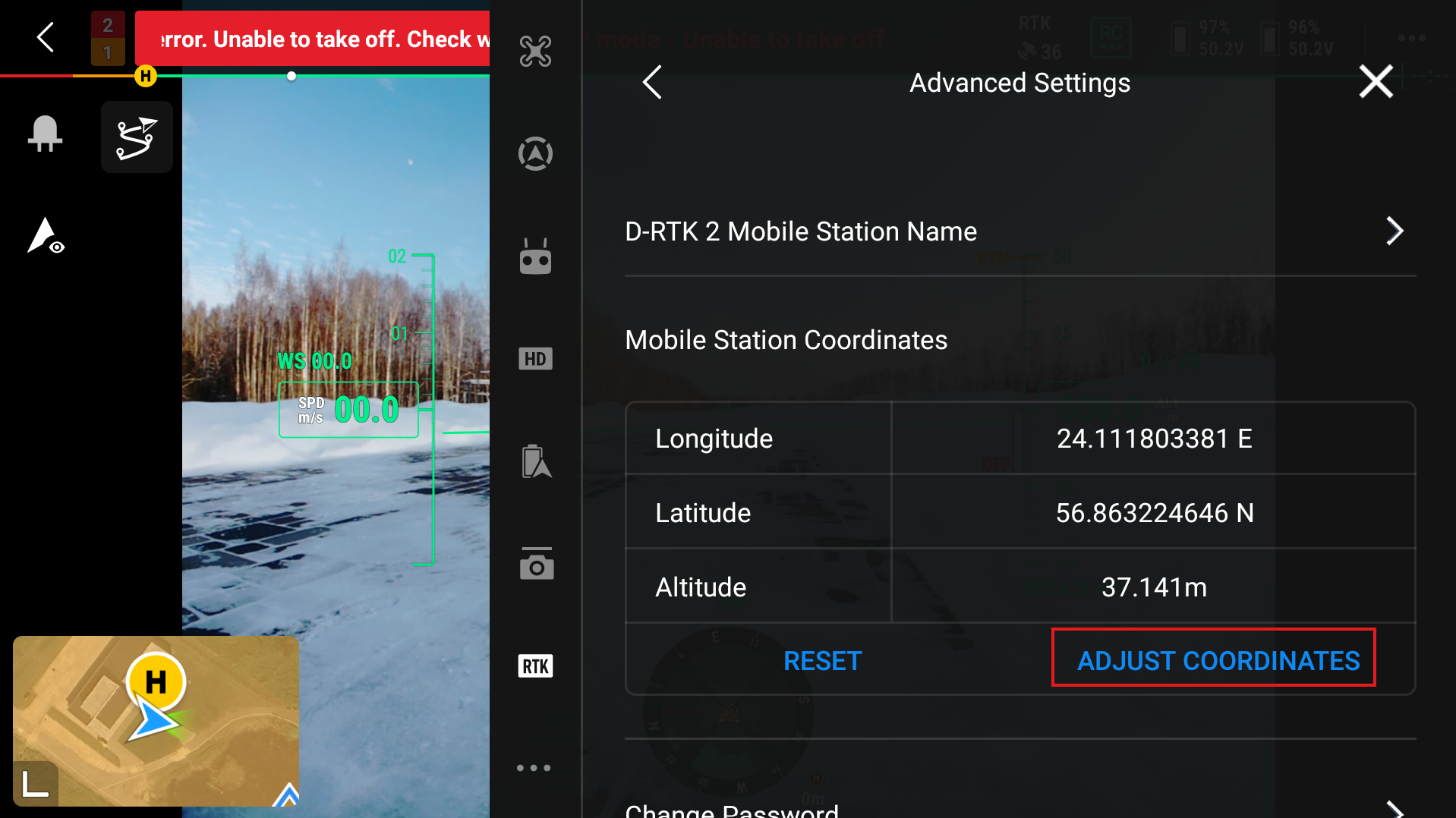
To put in the coordinates of your base station, go to the bottom of the screen and press Advanced settings. There you will be able to change the automatic coordinates of the D-RTK3 base station.
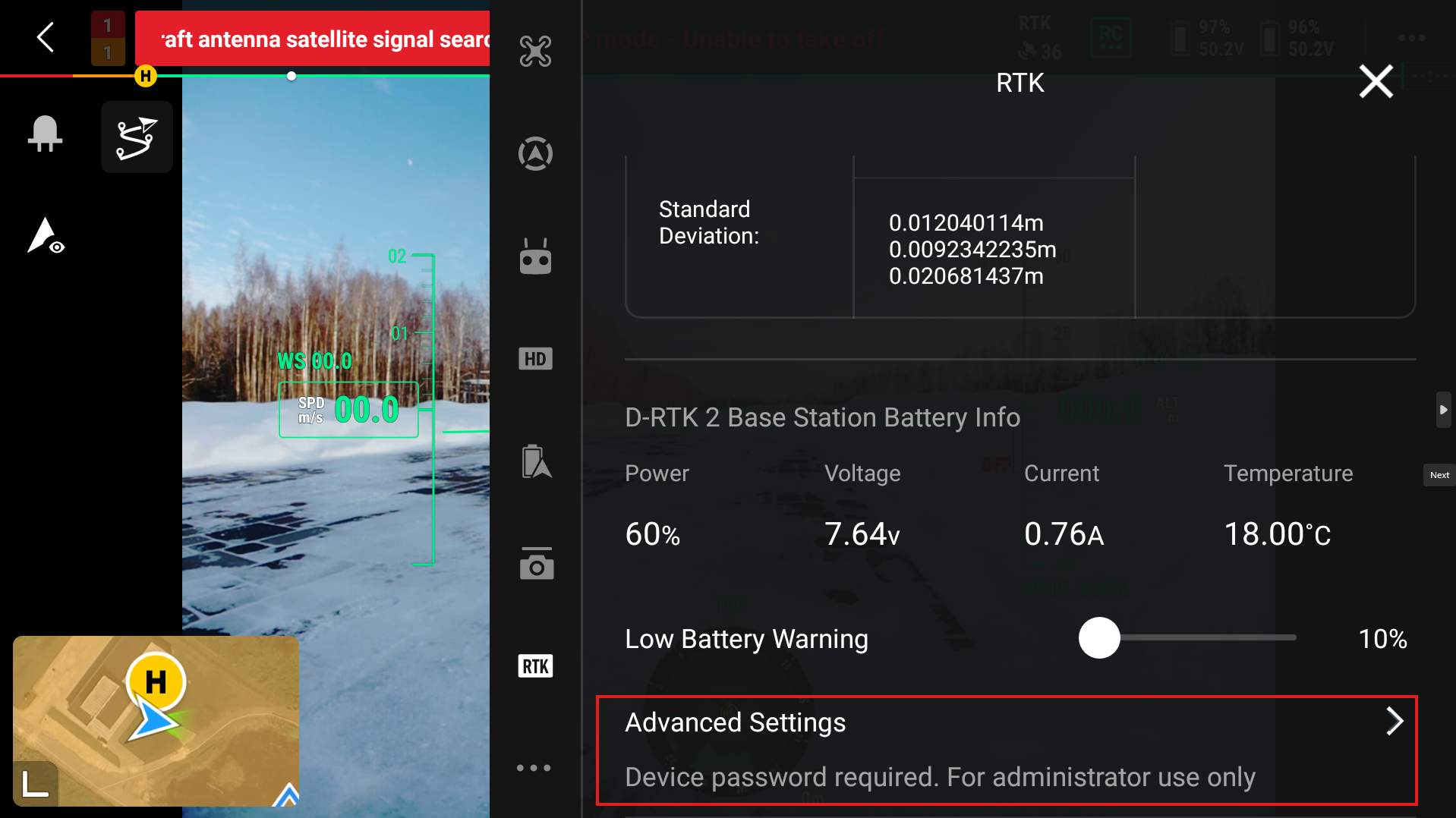
Then input the Longitude, Latitude and Altitude of the station.
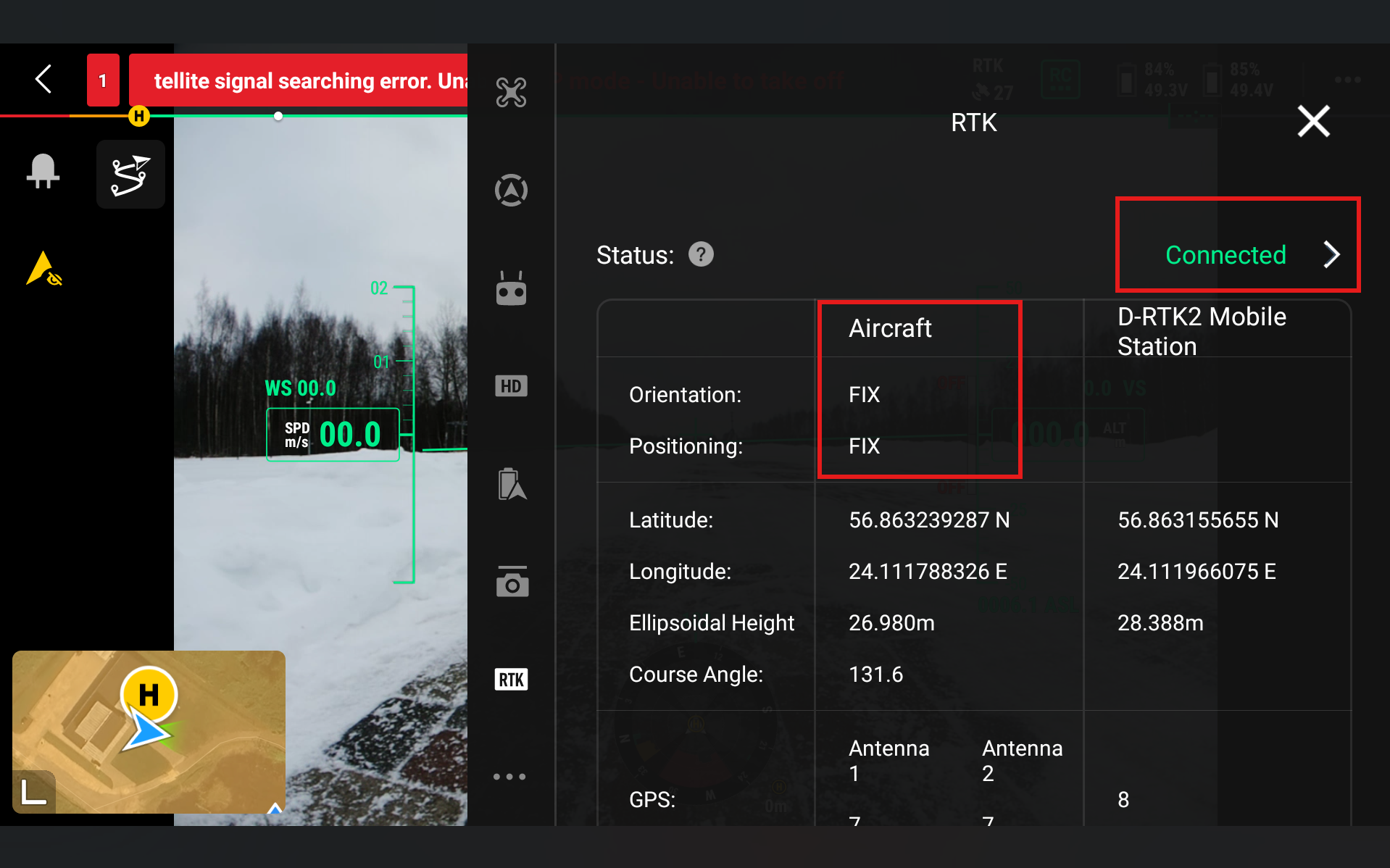
After setting up the base station the Aircraft RTK status should show FIX Positioning.
Now further information for if you are flying your mission with UgCS Companion. Firstly, close the DJI Pilot 2 application fully, so it is not running in the background. Then open up UgCS Companion and connect it to the drone as you normally would. If the drone is operational and ready to fly with RTK, it should show Ready to Go (RTK). And when pressing the RTK symbol at the top left of the screen, it shows RTK Status - Connected.

Note
If you are using an older version of UgCS Companion and when you click on the RTK symbol it shows RTK symbol - Unknown, then it is okay to continue only if the main screen in Companion shows Ready to Go RTK.
2.8. Operational Workflows#
Before flight, the operator should confirm that the D-RTK 3, aircraft, and controller firmware are up to date and that all devices are fully charged. The D-RTK 3 should be correctly configured in the required operating mode and positioned in an open area with clear sky visibility. Coordinate source and calibration method should be verified, and the connection between the D-RTK 3, controller, and aircraft should be established. Prior to takeoff, the RTK status displayed in DJI Pilot 2 should indicate an RTK Fix or Ready to Go (RTK) in UgCS Companion , and satellite signal strength should be sufficient.
During flight, the operator should continuously monitor RTK status and GNSS signal quality in the flight interface. Any transition from RTK Fix to Float or Non-RTK should be noted, as this may affect data accuracy. Stable communication links between the aircraft and the D-RTK 3 should be maintained.
After flight, recorded data should be reviewed to confirm that RTK positioning was maintained for the majority of the mission. Metadata, logs, or mission reports should be checked for RTK status information.
2.9. Troubleshooting#
Problem |
Fix |
|---|---|
RTK Fix cannot be achieved or is unstable |
Verify that the D-RTK 3 is placed in an open area with a clear view of the sky, away from obstacles. Firmware mismatches between the D-RTK 3, aircraft, and controller can prevent RTK fixes. Should be updated to compatible versions. |
Satellite count is low or signal strength is poor |
Waiting several minutes for satellite acquisition or repositioning the station may resolve the issue. |
Aircraft RTK Status - Converging for too long |
If the aircraft is inside, then that is expected, it will connect when it is outside with access to GNSS satellites. If the aircraft is outside and in a clear, non-obstructed area with access to GNSS satellites, then restart the drone and remote controller. |
UgCS companion shows Ready to Go (GPS) |
Wait for it to connect and receive more information from satellites. If waiting does not help, then try configuring the RTK again. |